Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia Is Killing Patients. Yet There Is a Simple Way to Stop It.
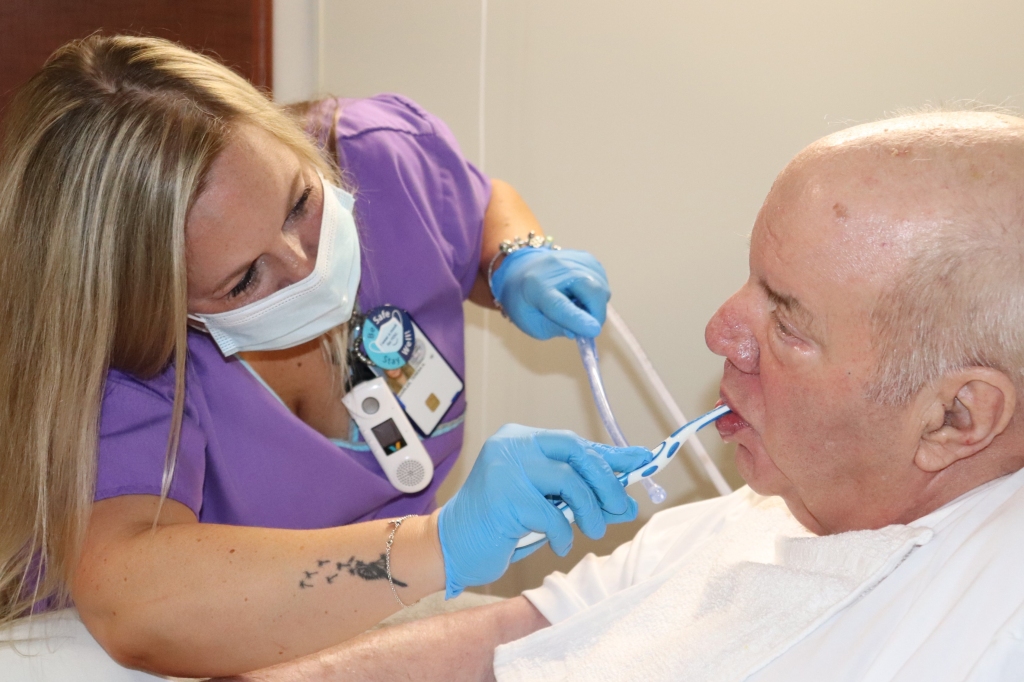
Four years ago, when Karen Giuliano went to a Boston hospital for hip replacement surgery, she was given a pale-pink bucket of toiletries issued to patients in many hospitals. Inside were tissues, bar soap, deodorant, toothpaste, and, without a doubt, the worst toothbrush she’d ever seen.
“I couldn’t believe it. I got a toothbrush with no bristles,” she said. “It must have not gone through the bristle machine. It was just a stick.”
To most patients, a useless hospital toothbrush would be a mild inconvenience. But to Giuliano, a nursing professor at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, it was a reminder of a pervasive “blind spot” in U.S. hospitals: the stunning consequences of unbrushed teeth.
Hospital patients not getting their teeth brushed, or not brushing their teeth themselves, is believed to be a leading cause of hundreds of thousands of cases of pneumonia a year in patients who have not been put on a ventilator. Pneumonia is among the most common infections that occur in health care facilities, and a majority of cases are non-ventilator hospital-acquired pneumonia, or NVHAP, which kills up to 30% of those infected, Giuliano and other experts said.
But unlike many infections that strike within hospitals, the federal government doesn’t require hospitals to report cases of NVHAP. As a result, few hospitals understand the origin of the illness, track its occurrence, or actively work to prevent it, the experts said.
Many cases of NVHAP could be avoided if hospital staffers more dutifully brushed the teeth of bedridden patients, according to a growing body of peer-reviewed research papers. Instead, many hospitals often skip teeth brushing to prioritize other tasks and provide only cheap, ineffective toothbrushes, often unaware of the consequences, said Dian Baker, a Sacramento State nursing professor who has spent more than a decade studying NVHAP.
“I’ll tell you that today the vast majority of the tens of thousands of nurses in hospitals have no idea that pneumonia comes from germs in the mouth,” Baker said.
Pneumonia occurs when germs trigger an infection in the lungs. Although NVHAP accounts for most of the cases associated with health care, it historically has not received the same attention as pneumonia tied to ventilators, which is easier to identify and study because it occurs among a narrow subset of patients.
NVHAP, a risk for virtually all hospital patients, is often caused by bacteria from the mouth that gathers in the scummy biofilm on unbrushed teeth and is aspirated into the lungs. Patients face a higher risk if they lie flat or remain immobile for long periods, so NVHAP can also be prevented by elevating their heads and getting them out of bed more often.
According to the National Organization for NV-HAP Prevention, which was founded in 2020, this pneumonia infects about 1 in every 100 hospital patients and kills 15% to 30% of them. For those who survive, the illness often extends their hospital stay by up to 15 days and makes it much more likely they will be readmitted within a month or transferred to an intensive care unit.
John McCleary, 83, of Bangor, Maine, contracted a likely case of NVHAP in 2008 after he fractured his ankle in a fall and spent 12 days in rehabilitation at a hospital, said his daughter, Kathy Day, a retired nurse and advocate with the Patient Safety Action Network.
McCleary recovered from the fracture but not from pneumonia. Two days after he returned home, the infection in his lungs caused him to be rushed back to the hospital, where he went into sepsis and spent weeks in treatment before moving to an isolation unit in a nursing home.
He died weeks later, emaciated, largely deaf, unable to eat, and often “too weak to get water through a straw,” his daughter said. After contracting pneumonia, he never walked again.
“It was an astounding assault on his body, from him being here visiting me the week before his fall, to his death just a few months later,” Day said. “And the whole thing was avoidable.”
While experts describe NVHAP as a largely ignored threat, that appears to be changing.
Last year, a group of researchers — including Giuliano and Baker, plus officials from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Veterans Health Administration, and the Joint Commission — published a “call-to-action” research paper hoping to launch “a national healthcare conversation about NVHAP prevention.”
The Joint Commission, a nonprofit organization whose accreditation can make or break hospitals, is considering broadening the infection control standards to include more ailments, including NVHAP, said Sylvia Garcia-Houchins, its director of infection prevention and control.
Separately, ECRI, a nonprofit focused on health care safety, this year pinpointed NVHAP as one of its top patient safety concerns.
James Davis, an ECRI infection expert, said the prevalence of NVHAP, while already alarming, is likely “underestimated” and probably worsened as hospitals swelled with patients during the coronavirus pandemic.
“We only know what’s reported,” Davis said. “Could this be the tip of the iceberg? I would say, in my opinion, probably.”
To better measure the condition, some researchers call for a standardized surveillance definition of NVHAP, which could in time open the door for the federal government to mandate reporting of cases or incentivize prevention. With increasing urgency, researchers are pushing for hospitals not to wait for the federal government to act against NVHAP.
Baker said she has spoken with hundreds of hospitals about how to prevent NVHAP, but thousands more have yet to take up the cause.
“We are not asking for some big, $300,000 piece of equipment,” Baker said. “The two things that show the best evidence of preventing this harm are things that should be happening in standard care anyway ― brushing teeth and getting patients mobilized.”
That evidence comes from a smattering of studies that show those two strategies can lead to sharp reductions in infection rates.
In California, a study at 21 Kaiser Permanente hospitals used a reprioritization of oral care and getting patients out of bed to reduce rates of hospital-acquired pneumonia by around 70%. At Sutter Medical Center in Sacramento, better oral care reduced NVHAP cases by a yearly average of 35%.
At Orlando Regional Medical Center in Florida, a medical unit and a surgical unit where patients received enhanced oral care reduced NVHAP rates by 85% and 56%, respectively, when compared with similar units that received normal care. A similar study is underway at two hospitals in Illinois.
And the most compelling results come from a veterans’ hospital in Salem, Virginia, where a 2016 oral care pilot program reduced rates of NVHAP by 92% — saving an estimated 13 lives in just 19 months. The program, the HAPPEN Initiative, has been expanded across the Veterans Health Administration, and experts say it could serve as a model for all U.S. hospitals.
Michelle Lucatorto, a nursing official who leads HAPPEN, said the program trains nurses to most effectively brush patients’ teeth and educates patients and families on the link between oral care and preventing NVHAP. While teeth brushing may not seem to require training, Lucatorto made comparisons to how the coronavirus revealed many Americans were doing a lackluster job of another routine hygienic practice: washing their hands.
“Sometimes we are searching for the most complicated intervention,” she said. “We are always looking for that new bypass surgery, or some new technical equipment. And sometimes I think we fail to look at the simple things we can do in our practice to save people’s lives.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).

